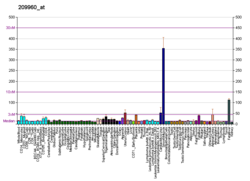
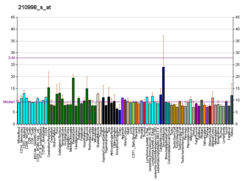
Facteur de croissance des hépatocytes

Pour les articles homonymes, voir HGF.
| HGF | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure de la protéine HGF. Basé sur l'identifiant PDB 1BHT. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | HGF, Facteur de croissance des hépatocytes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IDs externes | OMIM: 142409 MGI: 96079 HomoloGene: 503 GeneCards: HGF | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Le facteur de croissance des hépatocytes (Hepatocyte growth factor, HGF) est un facteur de croissance, agent mitogène des hépatocytes (cellules du foie). Il se lie au récepteur tyrosine kinase c-met (MET)[5]. Son gène est le HGF situé sur le chromosome 7 humain[5].
Inhibiteurs
Notes et références
- ↑ a b et c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000019991 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ a b et c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000028864 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ « Publications PubMed pour l'Homme », sur National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine
- ↑ « Publications PubMed pour la Souris », sur National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine
- ↑ a et b (en) George K. Michalopoulos et Reza Zarnegar, « Hepatocyte growth factor », Hepatology, vol. 15, no 1, , p. 149–155 (DOI 10.1002/hep.1840150125, lire en ligne, consulté le )
Bibliographie
- Michalopoulos GK, Zarnegar R, « Hepatocyte Growth Factor », Hepatology, vol. 15, no 1, , p. 149–54 (DOI 10.1002/hep.1840150125)
- Nakamura T, « Structure and function of hepatocyte growth factor », Prog. Growth Factor Res., vol. 3, no 1, , p. 67–85 (PMID 1838014, DOI 10.1016/0955-2235(91)90014-U)
- Ware LB, Matthay MA, « Keratinocyte and hepatocyte growth factors in the lung: roles in lung development, inflammation, and repair », Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol., vol. 282, no 5, , L924–40 (PMID 11943656, DOI 10.1152/ajplung.00439.2001)
- Funakoshi H, Nakamura T, « Hepatocyte growth factor: from diagnosis to clinical applications », Clin. Chim. Acta, vol. 327, nos 1–2, , p. 1–23 (PMID 12482615, DOI 10.1016/S0009-8981(02)00302-9)
- Skibinski G, « The role of hepatocyte growth factor/c-met interactions in the immune system », Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz.), vol. 51, no 5, , p. 277–82 (PMID 14626426)
- Kalluri R, Neilson EG, « Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis », J. Clin. Invest., vol. 112, no 12, , p. 1776–84 (PMID 14679171, PMCID 297008, DOI 10.1172/JCI20530)
- Hurle RA, Davies G, Parr C, MD Mason, SA Jenkins, HG Kynaston et WG Jiang, « Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor and prostate cancer: a review », Histol. Histopathol., vol. 20, no 4, , p. 1339–49 (PMID 16136515)
- Kemp LE, Mulloy B, Gherardi E, « Signalling by HGF/SF and Met: the role of heparan sulphate co-receptors », Biochem. Soc. Trans., vol. 34, no Pt 3, , p. 414–7 (PMID 16709175, DOI 10.1042/BST0340414)
Liens externes
- (en) MeSH Hepatocyte+growth+factor
- (en) Hepatocyte growth factor on the Atlas of Genetics and Oncology
- (en) UCSD Signaling Gateway Molecule Page on HGF
 Portail de la biochimie
Portail de la biochimie  Portail de la médecine
Portail de la médecine