| CDKN1A |
|---|
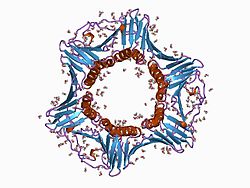 |
|
| Structures disponibles |
|---|
| PDB | Recherche d'orthologue: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| Identifiants PDB |
|---|
1AXC, 2ZVV, 2ZVW, 4RJF, 5E0U |
|
|
| Identifiants |
|---|
| Aliases | CDKN1A |
|---|
| IDs externes | OMIM: 116899 MGI: 104556 HomoloGene: 333 GeneCards: CDKN1A |
|---|
| Position du gène (Homme) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 6 humain[1] |
|---|
| | Locus | 6p21.2 | Début | 36,676,460 bp[1] |
|---|
| Fin | 36,687,339 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Position du gène (Souris) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 17 (souris)[2] |
|---|
| | Locus | 17 A3.3|17 15.12 cM | Début | 29,309,950 bp[2] |
|---|
| Fin | 29,319,701 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| Expression génétique |
|---|
| Bgee | | Humain | Souris (orthologue) |
|---|
| Fortement exprimé dans | - stromal cell of endometrium
- muqueuse gastrique
- veine cave
- left uterine tube
- cellule bêta
- aorte ascendante
- Veine saphène
- artère poplitée
- Tibial arteries
- Descending thoracic aorta
|
| | Fortement exprimé dans | - stroma of bone marrow
- calvaria
- molaire
- antre du pylore
- lèvre
- œsophage
- follicule pileux
- epithelium of stomach
- skin of external ear
- endothelial cell of lymphatic vessel
|
| | Plus de données d'expression de référence |
|
|---|
| BioGPS |  | | Plus de données d'expression de référence |
|
|---|
|
| Gene Ontology |
|---|
| Fonction moléculaire | - liaison ion métal
- liaison protéique
- cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity
- ubiquitin protein ligase binding
- cyclin binding
- cyclin-dependent protein kinase activating kinase activity
- cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- protein kinase inhibitor activity
- protein kinase binding
- liaison de complexe macromoléculaire
| | Composant cellulaire | - cytoplasme
- cytosol
- cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex
- PCNA-p21 complex
- perinuclear region of cytoplasm
- noyau
- nucléoplasme
- nucléole
- corps nucléaire
- complexe macromoléculaire
| | Processus biologique | - cellular response to extracellular stimulus
- signal transduction by p53 class mediator
- intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator
- cellular response to heat
- regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest
- positive regulation of cell death
- response to organic cyclic compound
- negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- stress-induced premature senescence
- positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation
- replicative senescence
- response to hyperoxia
- response to corticosterone
- cellular response to amino acid starvation
- positive regulation of programmed cell death
- negative regulation of apoptotic process
- response to glucocorticoid
- response to arsenic-containing substance
- regulation of DNA biosynthetic process
- response to organic substance
- negative regulation of gene expression
- cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
- negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle
- régulation du cycle cellulaire
- intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway
- sénescence cellulaire
- positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process
- cellular response to UV-B
- G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle
- positive regulation of B cell proliferation
- negative regulation of cell growth
- response to organonitrogen compound
- animal organ regeneration
- regulation of mitotic cell cycle
- intestinal epithelial cell maturation
- cellular response to ionizing radiation
- cycle cellulaire
- Ras protein signal transduction
- negative regulation of phosphorylation
- réponse à une substance toxique
- response to UV
- response to X-ray
- negative regulation of cell population proliferation
- protein stabilization
- positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity
- regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in transcription of p21 class mediator
- positive regulation of protein kinase activity
- cellular response to gamma radiation
- negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity
- transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter
- G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle
- cytokine-mediated signaling pathway
- negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologues |
|---|
| Espèces | Homme | Souris |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_078467
NM_000389
NM_001220777
NM_001220778
NM_001291549 |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protéine) | NP_000380
NP_001207706
NP_001207707
NP_001278478
NP_510867
|
|---|
NP_001361438
NP_001361439
NP_001361440
NP_001361441
NP_001361442 |
| |
|---|
| Localisation (UCSC) | Chr 6: 36.68 – 36.69 Mb | Chr 17: 29.31 – 29.32 Mb |
|---|
| Publication PubMed | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| Voir/Editer Humain | Voir/Editer Souris |
|


 Portail de la biologie
Portail de la biologie 
















