| PTPN22 |
|---|
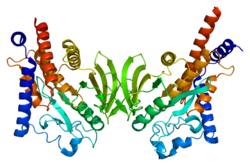 |
| Structure de la protéine PTPN22. Basé sur l'identifiant PDB 2p6x. |
| Structures disponibles |
|---|
| PDB | Recherche d'orthologue: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| Identifiants PDB |
|---|
2P6X, 2QCJ, 2QCT, 3BRH, 3H2X, 3OLR, 3OMH, 4J51 |
|
|
| Identifiants |
|---|
| Aliases | PTPN22, Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non receptor type 22 |
|---|
| IDs externes | OMIM: 600716 MGI: 107170 HomoloGene: 7498 GeneCards: PTPN22 |
|---|
| Position du gène (Homme) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 1 humain[1] |
|---|
| | Locus | 1p13.2 | Début | 113,813,811 bp[1] |
|---|
| Fin | 113,871,753 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Position du gène (Souris) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 3 (souris)[2] |
|---|
| | Locus | 3|3 F2.2 | Début | 103,767,111 bp[2] |
|---|
| Fin | 103,819,563 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| Expression génétique |
|---|
| Bgee | | Humain | Souris (orthologue) |
|---|
| Fortement exprimé dans | - cellule de la moelle osseuse
- monocyte
- sang
- tendon calcanéen
- artère temporale superficielle
- ganglion lymphatique
- rate
- appendice iléo-cæcal
- muqueuse jéjunale
- os spongieux
|
| | Fortement exprimé dans | - thymus
- rate
- ganglion lymphatique
- sang
- secondary oocyte
- morula
- subcutaneous adipose tissue
- spermatocyte
- moelle osseuse
- Jéjunum
|
| | Plus de données d'expression de référence |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 
 | | Plus de données d'expression de référence |
|
|---|
|
| Gene Ontology |
|---|
| Fonction moléculaire | - phosphoprotein phosphatase activity
- SH3 domain binding
- phosphatase activity
- liaison de kinase
- liaison protéique
- activité hydrolase
- ubiquitin protein ligase binding
- protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
| | Composant cellulaire | - cytoplasme
- perinuclear region of cytoplasm
- cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane
- noyau
- cytosol
| | Processus biologique | - positive regulation of protein K63-linked ubiquitination
- regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling
- regulation of innate immune response
- regulation of natural killer cell proliferation
- positive regulation of toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway
- regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway
- regulation of B cell receptor signaling pathway
- phosphoanandamide dephosphorylation
- processus du système immunitaire
- negative regulation of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 signaling pathway
- negative regulation of p38MAPK cascade
- protein dephosphorylation
- negative regulation of gene expression
- negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway
- cellular response to muramyl dipeptide
- autophagie
- response to lipopolysaccharide
- T cell differentiation
- positive regulation of gene expression
- positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade
- positive regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway
- negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production
- negative regulation of autophagy
- negative regulation of JUN kinase activity
- negative regulation of T cell activation
- positive regulation of type I interferon production
- lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway
- dephosphorylation
- peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation
- T cell receptor signaling pathway
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologues |
|---|
| Espèces | Homme | Souris |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001193431
NM_001308297
NM_012411
NM_015967 |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protéine) | |
|---|
NP_001180360
NP_001295226
NP_036543
NP_057051 |
| |
|---|
| Localisation (UCSC) | Chr 1: 113.81 – 113.87 Mb | Chr 3: 103.77 – 103.82 Mb |
|---|
| Publication PubMed | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| Voir/Editer Humain | Voir/Editer Souris |
|
PTPN22 pour « Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non receptor type 22 », est une protéine tyrosine phosphatase (LYP) exprimée dans les tissus lymphoïdes et codée par le gène PTPN22[5] situé sur le chromosome 1 humain.
Le gène PTPN22
PTPN22 est un gène de 57 949 paires de bases situé sur le chromosome 1 en position 1p13.2 et composé de 21 exons[6]. Il est exprimé dans les tissus lymphoïdes et code quatre isoformes traduites de manière indépendante à la suite d'un épissage alternatif[6],[7]. LYP1, l'isoforme la plus documentée, est une protéine de 807 acides aminés ayant un poids moléculaire de 105 kD. Elle est composée de 3 domaines majeurs. Un domaine catalytique tyrosine phosphatase (PTP)en N-terminal, un domaine intermédiaire et un domaine C-terminal composé de 4 motifs riches en prolines, appelés P1 à P4[8].
Rôles et fonctions de la protéine PTPN22
La protéine PTPN22 ou LYP est localisée principalement dans le cytosol des cellules immunitaires, où elle est impliquée dans de nombreuses voies de signalisation associées à la réponse immunitaire. Son action se situe principalement au niveau des voies de signalisation des récepteurs des lymphocytes T (TCR) et lymphocytes B (BCR) où elle joue un rôle important d’inhibiteur de l'activation et de la prolifération lymphocytaire. Le role de LYP est principalement décrit dans la signalisation du TCR[9].
En médecine
Cette phosphatase joue un rôle de régulateur négatif de l'activation des lymphocytes T à travers une inhibition de la voie de signalisation de leur récepteur, le TCR. Une mutation au sein du gène PTPN22 a été associée à diverses maladies auto-immunes dont le diabète de type 1[10] et la polyarthrite rhumatoïde[11].
La protéine est surexprimée dans le syndrome coronarien aigu entraînant une baisse des lymphocytes T régulateurs[12].
Notes et références
- ↑ a b et c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000134242 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ a b et c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027843 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ « Publications PubMed pour l'Homme », sur National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine
- ↑ « Publications PubMed pour la Souris », sur National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine
- ↑ Cohen S, Dadi H, Shaoul E, Sharfe N, Roifman CM, Cloning and characterization of a lymphoid-specific, inducible human protein tyrosine phosphatase, Lyp, Blood, 1999;15;2013-24
- ↑ a et b Wang S, Dong H, Han J et al. Identification of a variant form of tyrosine phosphatase LYP, BMC Mol Biol, 2010;11:78
- ↑ Chang HH, Tai TS, Lu B et al. PTPN22.6, a dominant negative isoform of PTPN22 and potential biomarker of rheumatoid arthritis, PLoS One, 2012;7:e33067
- ↑ Burn GL, Svensson L, Sanchez-Blanco C, Saini M, Cope AP, Why is PTPN22 a good candidate susceptibility gene for autoimmune disease?, FEBS Lett, 2011;585:3689-98
- ↑ Bottini N, Peterson EJ, Tyrosine phosphatase PTPN22: multifunctional regulator of immune signaling, development, and disease, Annu Rev Immunol, 2014;32:83-119
- ↑ Bottini N, Musumeci L, Alonso A et al. A functional variant of lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase is associated with type I diabetes, Nat Genet, 2004;36:337-8
- ↑ van Oene M1, Wintle RF, Liu X et al. Association of the lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase R620W variant with rheumatoid arthritis, but not Crohn's disease, in Canadian populations, Arthritis Rheum, 2005;52:1993-8
- ↑ Flego D, Severino A, Trotta F et al. Increased PTPN22 expression and defective CREB activation impair regulatory T-cell differentiation in non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes, J Am Coll Cardiol, 2015;65:1175–1186
 Portail de la médecine
Portail de la médecine  Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire
Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire

 Portail de la médecine
Portail de la médecine  Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire
Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire 
















